-
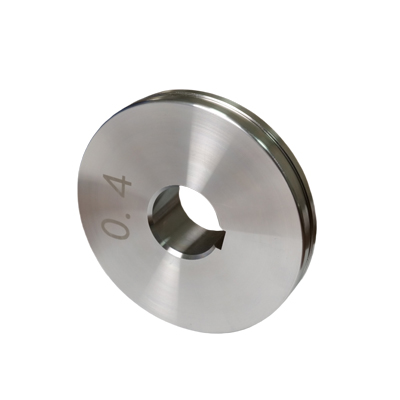
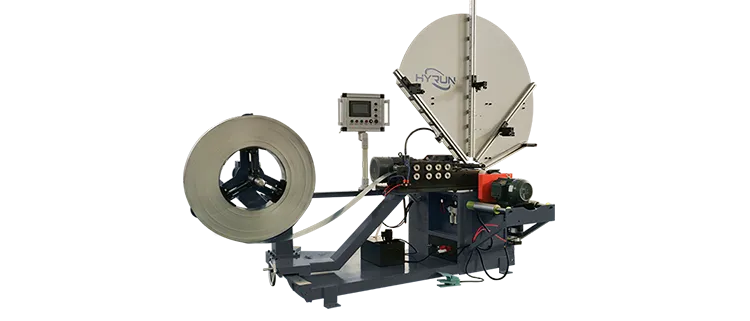
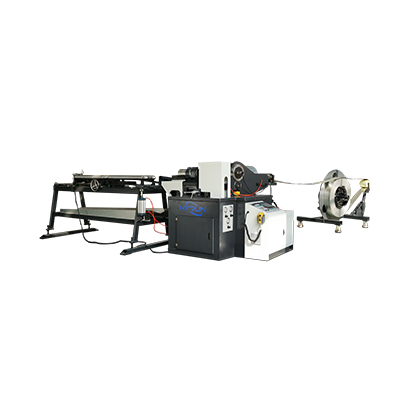 Tube Mold Spiral Duct Machine
Tube Mold Spiral Duct Machine
-
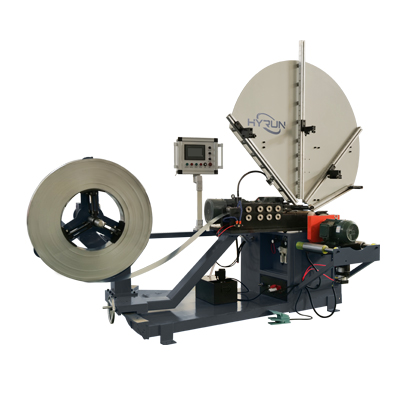 Steel Belt Spiral Duct Machine With 4 Sets Forming Rollers
Steel Belt Spiral Duct Machine With 4 Sets Forming Rollers
-
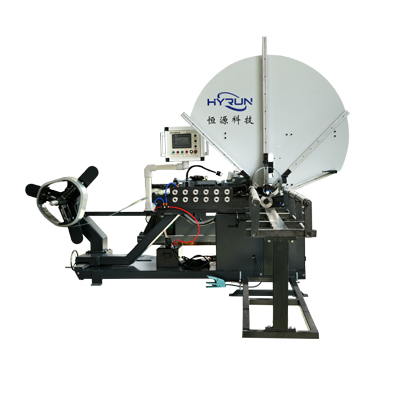 Steel Belt Spiral Duct Machine With 6 Sets Forming Rollers
Steel Belt Spiral Duct Machine With 6 Sets Forming Rollers
-
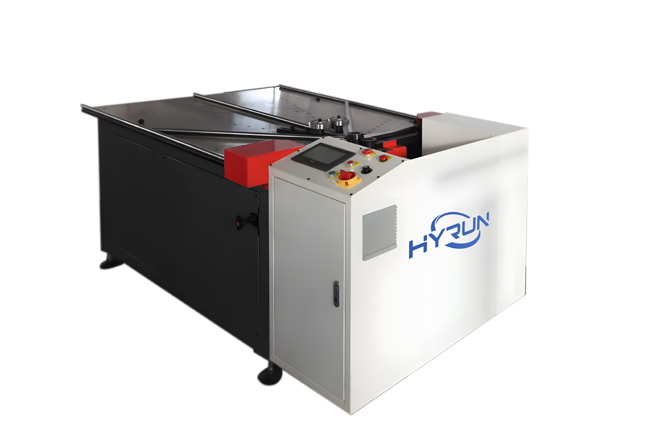
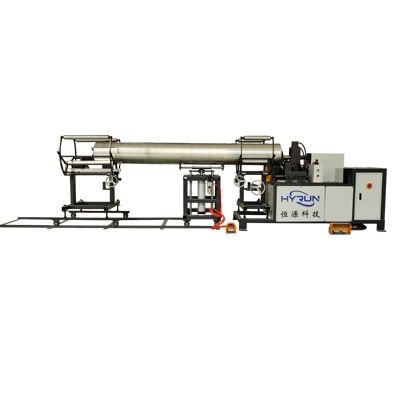 Spiral Duct Flanging Machine
Spiral Duct Flanging Machine
-
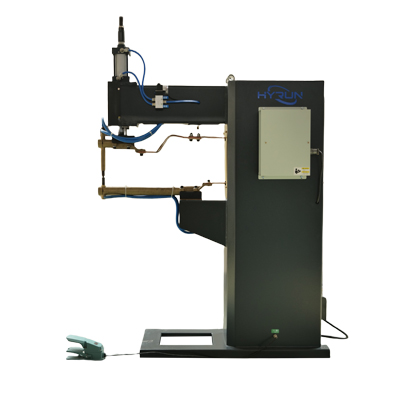 Pneumatic Spot Welding Machine
Pneumatic Spot Welding Machine
-
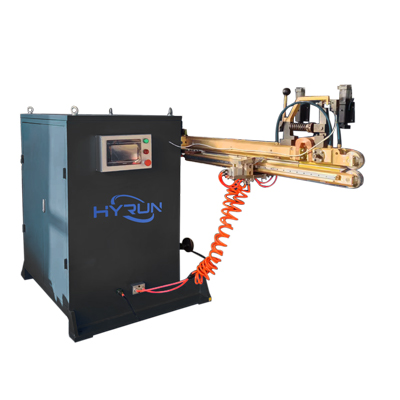 Seam Stitch Welding Machine
Seam Stitch Welding Machine
-
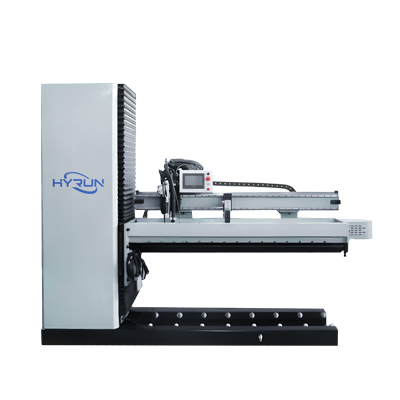 Straight Seam Automatic Welding Machine
Straight Seam Automatic Welding Machine
-
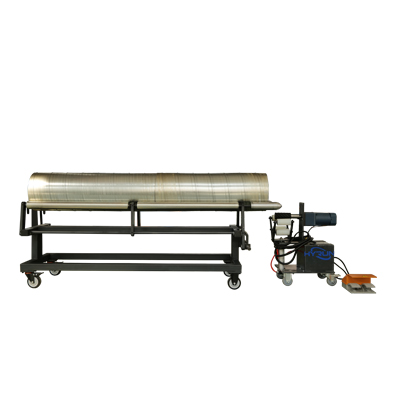 Duct Connection Welding Rack
Duct Connection Welding Rack
-
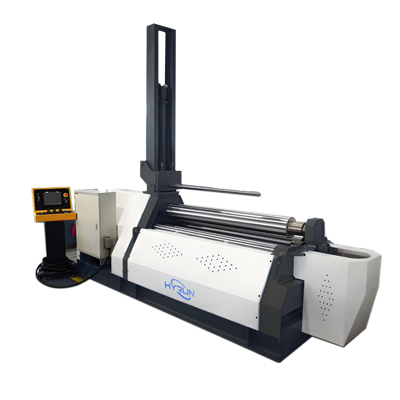 4-Roller Plate Rolling Machine
4-Roller Plate Rolling Machine
-
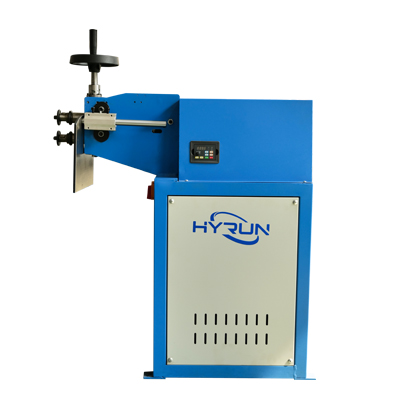 Reel Machine
Reel Machine
-
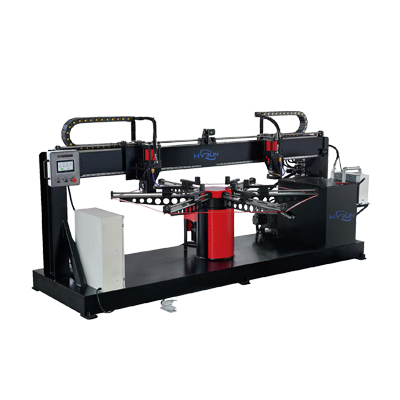 Round Duct Flange Punching Machine
Round Duct Flange Punching Machine
-
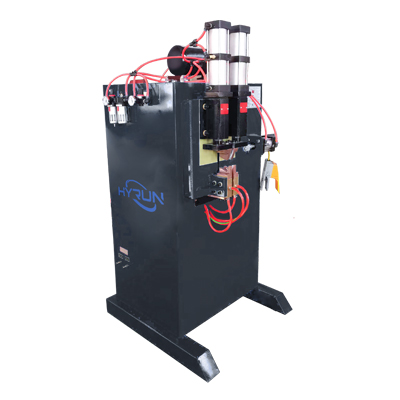 Round Flange Welding Machine
Round Flange Welding Machine
-
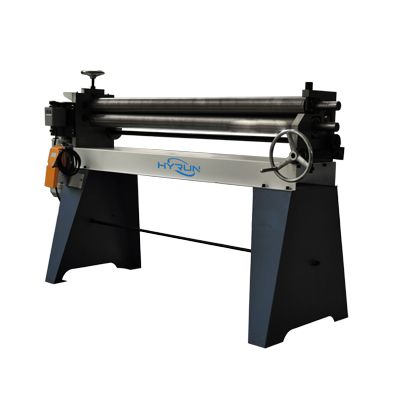 Asymmetrical 3-Roller Bending Machine
Asymmetrical 3-Roller Bending Machine
-
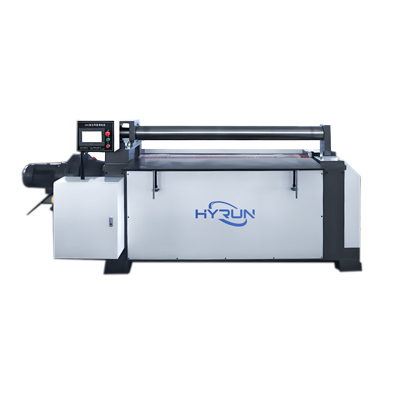 Hydraulic Rolling Machine
Hydraulic Rolling Machine
-
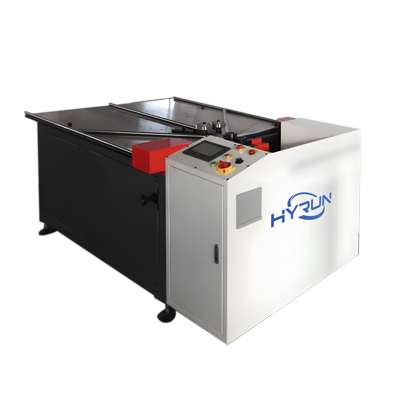 Hydraulic Flange Forming Machine
Hydraulic Flange Forming Machine
-
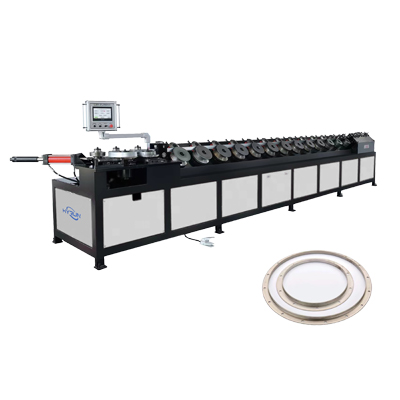 Round Duct Flange Forming Machine
Round Duct Flange Forming Machine
-
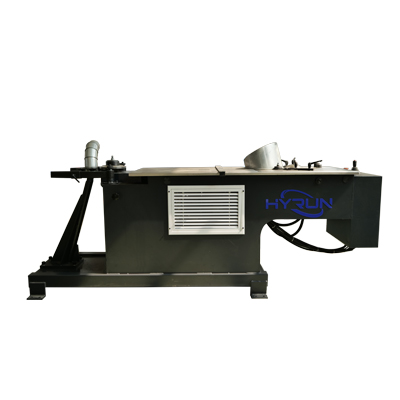 Hydraulic Elblow Machine
Hydraulic Elblow Machine
-
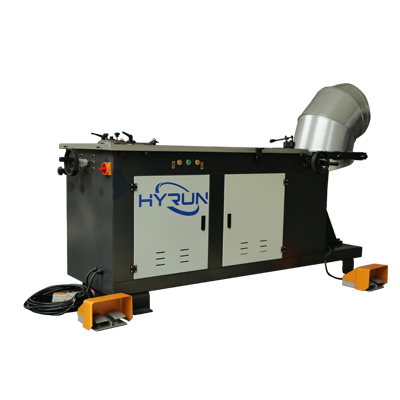 Electric Elbow Duct Machine
Electric Elbow Duct Machine
-
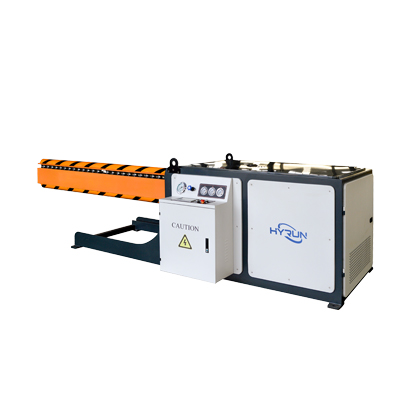 Oval Duct Machine
Oval Duct Machine
-
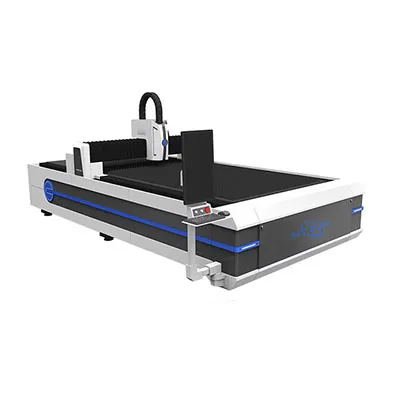 CNC Laser Cutting Machine
CNC Laser Cutting Machine
-
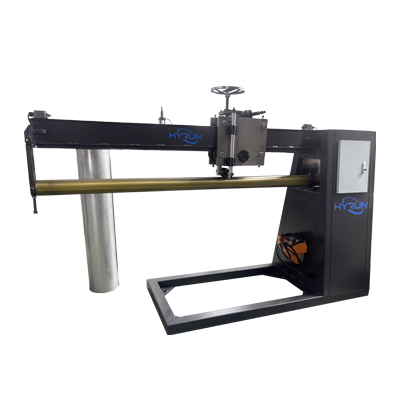 Round Duct Seam Closing Machine
Round Duct Seam Closing Machine
-
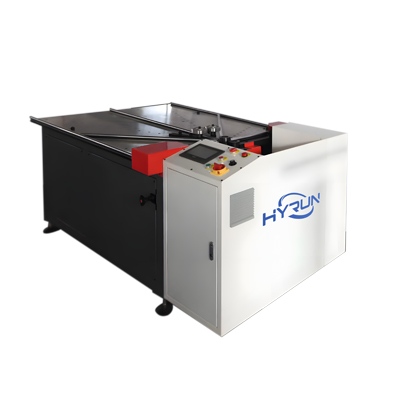 Hydraulic Round Duct Edge Forming Machine
Hydraulic Round Duct Edge Forming Machine
-
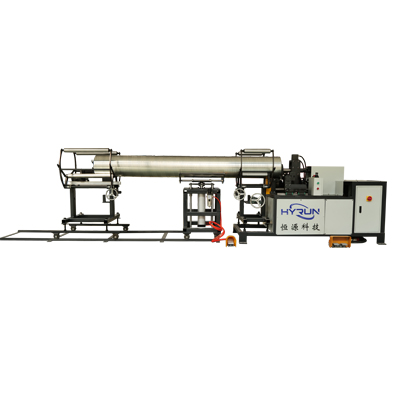 Spiral Duct Edge Forming Machine
Spiral Duct Edge Forming Machine
-
 Tube Mold Spiral Duct Machine
Tube Mold Spiral Duct Machine
-
 Spiral Duct Flanging Machine
Spiral Duct Flanging Machine
-
 Steel Belt Spiral Duct Machine With 4 Sets Forming Rollers
Steel Belt Spiral Duct Machine With 4 Sets Forming Rollers
-
 Steel Belt Spiral Duct Machine With 6 Sets Forming Rollers
Steel Belt Spiral Duct Machine With 6 Sets Forming Rollers
-
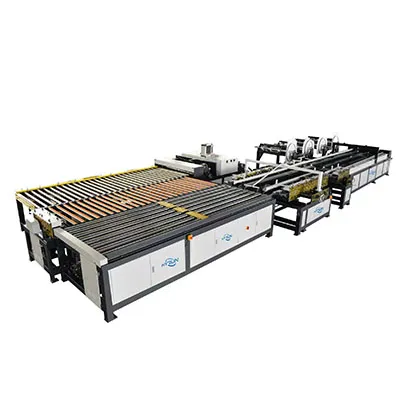 Auto Duct Line 5
Auto Duct Line 5
-
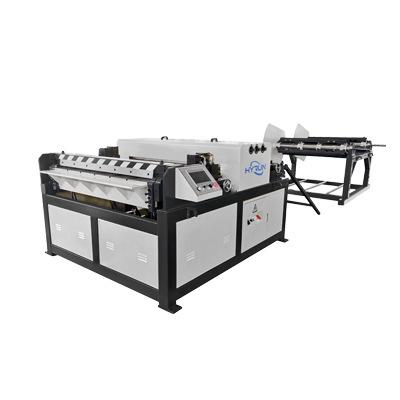 Auto Duct Line 3
Auto Duct Line 3
-
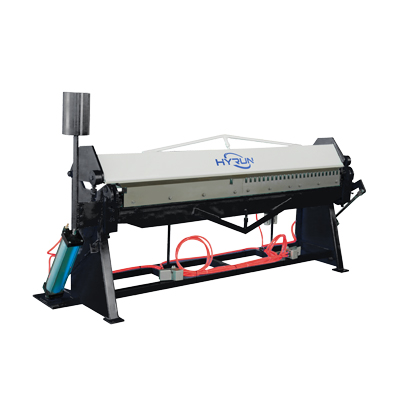 Pneumatic Folding Machine
Pneumatic Folding Machine
-
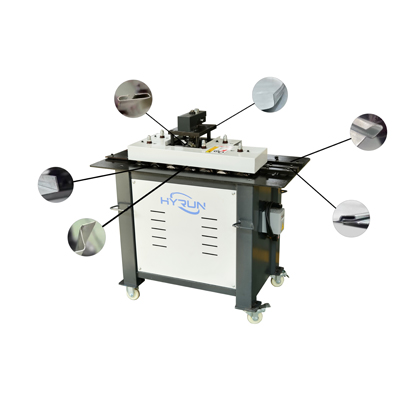 Lock Forming Machine
Lock Forming Machine
-
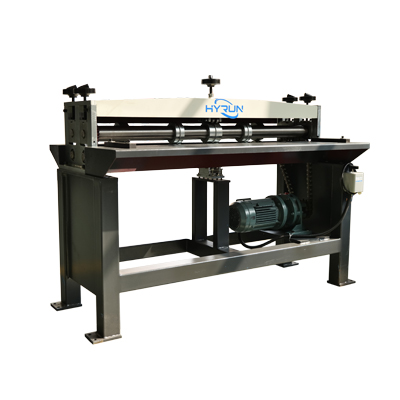 Grooving Machine
Grooving Machine
-
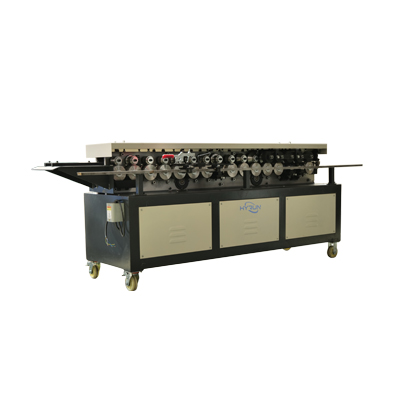 TDF Flange Forming Machine
TDF Flange Forming Machine
-
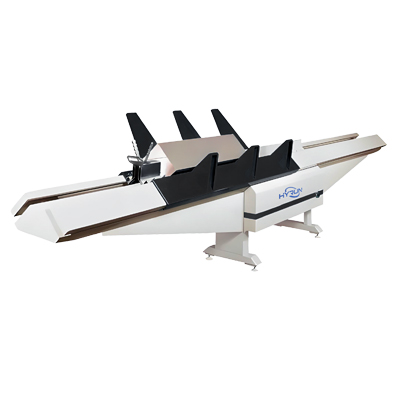 Square Duct Seam Closing Machine
Square Duct Seam Closing Machine
-
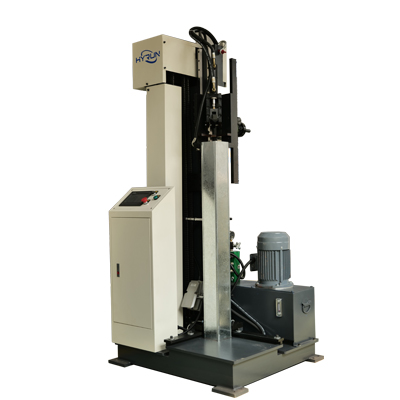 Hydraulic Seam Closing Machine
Hydraulic Seam Closing Machine
-
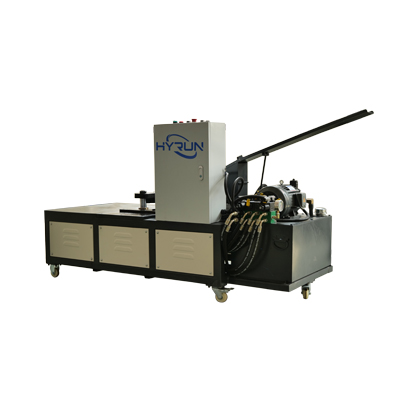 Corner Binding Machine
Corner Binding Machine
-
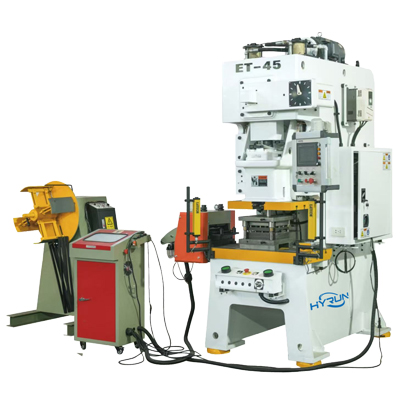 Corner Production Line
Corner Production Line
-
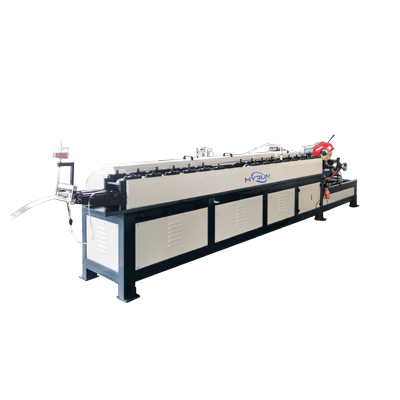 TDC Flange Forming Machine
TDC Flange Forming Machine
-
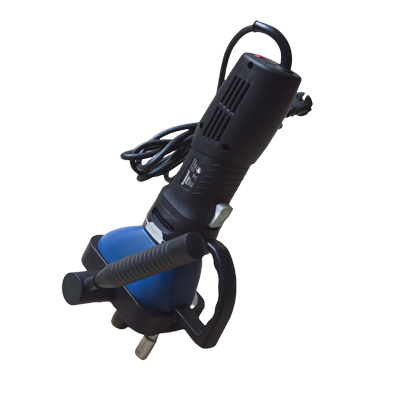 Electric Seam Closing Machine
Electric Seam Closing Machine
-
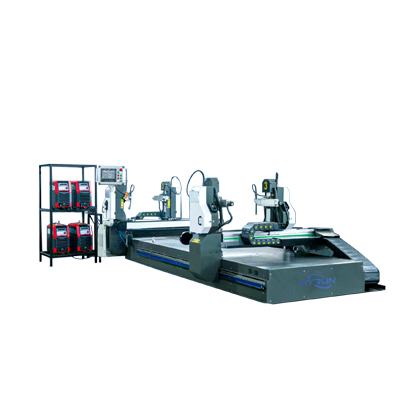 Angle Steel Flange Welding Machine
Angle Steel Flange Welding Machine
-
 Round Flange Welding Machine
Round Flange Welding Machine
-
 Pneumatic Spot Welding Machine
Pneumatic Spot Welding Machine
-
 Seam Stitch Welding Machine
Seam Stitch Welding Machine
-
 Straight Seam Automatic Welding Machine
Straight Seam Automatic Welding Machine
-
 Duct Connection Welding Rack
Duct Connection Welding Rack
-
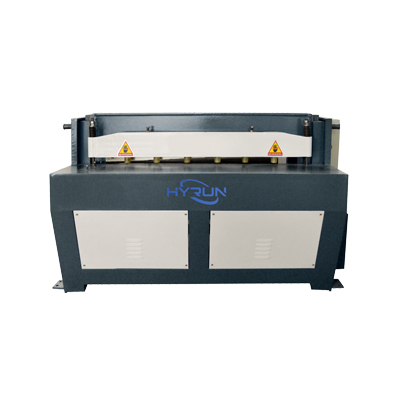 Electric Shearing Machine
Electric Shearing Machine
-
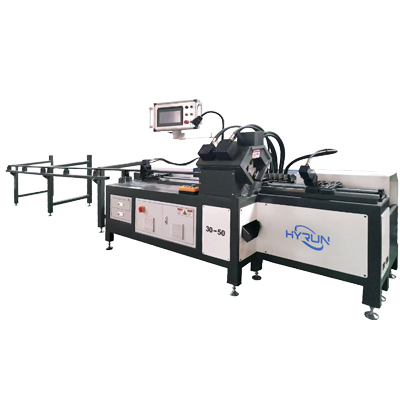 Angle Steel Punching Machine
Angle Steel Punching Machine
-
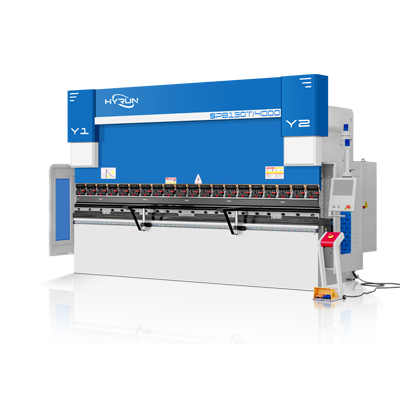 CNC Press Brake
CNC Press Brake
-
 CNC Laser Cutting Machine
CNC Laser Cutting Machine
-
 Asymmetrical 3-Roller Bending Machine
Asymmetrical 3-Roller Bending Machine
-
 Hydraulic Rolling Machine
Hydraulic Rolling Machine
-
 Pneumatic Folding Machine
Pneumatic Folding Machine
-
 Lock Forming Machine
Lock Forming Machine
-
 4-Roller Plate Rolling Machine
4-Roller Plate Rolling Machine
-
 Reel Machine
Reel Machine
-
 Round Duct Flange Punching Machine
Round Duct Flange Punching Machine
-
 Grooving Machine
Grooving Machine
-
 Hydraulic Round Duct Edge Forming Machine
Hydraulic Round Duct Edge Forming Machine
WHAT ARE YOU LOOKING FOR?